Exhaust Standards 2014
Clean Air is Important! What the European Exhaust Standards Mean for YouStrict criteria have been put in place concerning the manufacture of Engine driven forklifts. These are intended to improve energy and fuel efficiency as well as to reduce pollutant emissions.
Since January 1, 2014, the Euro 6 norm applies within Europe. The goal is to reduce the emission of particulate matter by 66% and nitrogen oxide by 80%. This means, for instance, that all new Diesel engine driven vehicles which are being registered must be equipped so that they meet these standards.
The lowering of the maximum permissable values also applies to vehicles being used for in-house logistic operations. Since 2013, the maximum permissible values have been set by European regulation 97/68/EG stage IIIb. These values apply mainly to the emission of nitrogen oxide (NOx), carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC) as well as fine particulate matter such as diesel soot (PM).
What does stage IIIb mean?
The current stage IIIb lays down tougher guidelines for Diesel engines with a power output of more than 37 kW. In practice, all Diesel engine trucks which have a capacity of 2.5 tonnes or more are affected. The incremental implementation of IIIb relates to performance classes measured in kW.
Stage IIIb sets a limit of 0.025 g per KW/H for particulate matter and a 3.3 g per KW/H maximum of hydrogen oxide emissions for engines up to 130 KW (177 horsepower).
What you need to know about Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs)
In order to meet emission standard demands, many manufacturers are implementing DPFs which remove soot and contaminants from exhaust before emission occurs.
In general, DPFs may be divided into two groups:
- Classic Torch System
- CRT-Filter System (Continuously-Regenerating-Trap-Filter System)
Classic systems filter a majority of the Diesel particulates that are generated during the combustion process from the exhaust. A conventional particle filter needs to be regenerated after every eight to ten hours of typical forklift operation. It must also be serviced after 1000 hours and replaced completely from time to time. During regeneration, the filter is torched. During this time the truck is unavailable for about 30 minutes.
During the torching process, hydrocarbons are created which, in turn, are then released without being filtered or are transformed into harmful dioxins.
The use of classic torch systems has negative effects both in terms of forklift availability as well as servicing expense.
A CRT filter is a high quality filter system with the decisive advantage that the filter does not require cleaning (torching) but, rather, cleanses and regenerates itself continually while it is in use.
A CRT filter system ensures both greater availability of the forklift as well as the meeting of the legal emission standards.
How it works:
Diesel Particle Filters with Torch Systems

Inside a DPF using a torch system the exhaust is pressed into corridors with dead ends. The walls of these corridors are gas permeable: The filtered exhaust passes through but the pollutants remain behind, trapped within these chambers.
CRT Filter System
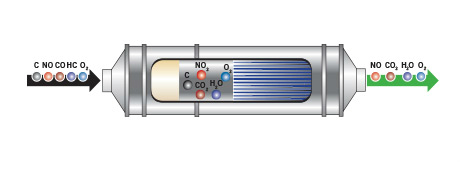
A CRT filter regenerates itself while it is in operation. The soot particles are held within the filter and torched continuously. When possible this is done in combination with an oxidation catalytic converter: the nitrous dioxide (NO2) which forms in the converter allows for the continual burning of the particulates within the filter.
STILL already has the answers to the stricter emissions standards of tomorrow
Intelligent Compliance with New Emissions StandardsSTILL believes that minimizing the amount of harmful pollutants which are created in the first place is even better than efficiently filtering them from the truck's exhaust.
An imporant characteristic of all drive technologies used in RX 70 models is their excellent energy efficiency: The truck's engine powers a generator which, in turn, supplies electricity to the drive motor. During all of this, the engine operates at the minimum rpm range required for the performance demanded. This means that both extremely low fuel consumption and pollutant emission levels are achieved. This is also the reason why only the RX 70, the largest in the family with a capacity of up to 8 tonnes, is equipped with a particle filter. All of the other engine trucks in the series lie well within the legal standards and norms without any need for particle filter systems.
In order to further minimize pollutant emissions, all RX 70 models are also available with an optional, additional diesel particulate filter.
The critical question when buying a forklift: "Electric or Engine?"
The key to deciding lies in the vehicle's operational profile
What are the strengths of electric and combustion motor forklifts? Which type of truck is best suited for different areas of use? And under which conditions do the different trucks provide the greatest potential for savings?


